
Original Article: The Effect of a Polyherbal Oral Formulation in the Management of Essential Hypertension: An Open Label, Pilot Clinical Study Journal: International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology (IJBCP) Clinical Study: www.ijbcp.com, July 2018 | Vol 7 | Issue 7 Page 1427 Click to Download Full Research Paper Journal Published Link: http://www.ijbcp.com/index.php/ijbcp/article/view/2566/2007 Abstract Background: Effective control of blood pressure in patients with hypertension decreases cardiovascular mortality. However, many hypertensives are unresponsive to standard antihypertensive treatment. Research has found antihypertensive potential in the Ayurvedic drugs Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri) and Shunthi (Zingiber officinale). Hence, a pilot study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Capsule Artyl (the oral formulation of Brahmi and Shunthi) as a treatment option in hypertensive subjects. Methods: There were 30 hypertensive subjects attending out-patient departments of clinics in Maharashtra, India were enrolled in this four-week, open label, single arm study. All subjects received capsule Artyl (500mg) twice a day orally daily. The mean systolic (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) on days 1 and 28 of the study were compared along with the mean arterial pressure (MAP). Results: The mean SBP was significantly lesser on day 28 (141.86±12.54mm Hg) as compared to the mean SBP recorded on day 1 (155.48±19.37mm Hg) (p<0.001). The mean DBP on day 28 (89.66±6.8mm Hg) was lesser than that on day 1 (90.34±7.44mm Hg) but this difference was not statistically significant (p>0.05). There was a significant decrease in the mean value of MAP on day 28 (107.06±7.03mm Hg) as compared to that on day 1 (112.06±10.75mm Hg) (p<0.01). Conclusions: Capsule Artyl significantly decreased the BP in hypertensive patients, without any adverse effects. Controlled trials are needed to confirm the positive outcome of this promising herbal formulation in hypertensive patients. Keywords: Capsule artyl, Essential hypertension, Systolic blood pressure
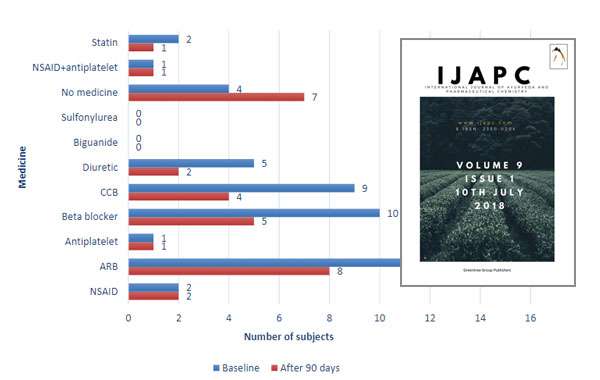
Original Article: To Study Efficacy of Blood Pressure Management Program in Overweight to Obese Male Patients with Known History of Hypertension: A retrospective study Journal: International Journal of Ayurveda and Pharmaceutical Chemistry Clinical Study: Int J Ayu Pharm Chem 2018 Vol. 9 Issue 1 Click to Download Full Research Paper Journal Published Link: http://www.ijapc.com/volume9-first-issue/MNAPC-V9-I1-65-p-412-425.pdf Abstract Background and Objective: Hypertension is the leading cause of global burden of cardiovascular disease. It is an epidemic that globally affects one billion people and a common cause of death. This retrospective study was conducted in April 2017 to evaluate the effect of the Blood Pressure (BP) Management Program in overweight to obese category male hypertensive patients. Methods: Data of 28 patients were included who had received the scheduled 6 sitting of BP management kit in a span of 90 days. In this study, the variables [mean systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mean arterial pressure (MAP), Body Mass Index (BMI) and dependency of allopathic medicines] were assessed on day 1 to day 90 of the BP management program. Results: The mean SBP was significantly lower on day 90 (153.5 ± 9.6 mm Hg to 127.80± 10.23 mm Hg, (p<0.001). The mean DBP reduced significantly from day 1 (91.60 ± 9.13 mm Hg to 78.64 ± 6.92 mm Hg). The mean value of MAP was much lower on day 90 (112.21 ± 7.3 5mm Hg to 94.80 ± 7.44 mm Hg, p<0.01). The BMI was much lower from day 1 (27.47 ± 2.49 to 26.45 ± 2.21, P < 0.001). Patients dependent on allopathic medicines were lesser at 90 days. Conclusions: The BP management program was efficacious in controlling hypertension in male patients that were overweight or obese. KEYWORDS: Blood pressure management, Alternative medicine, Panchakarma, Ayurveda

Original Article: To Study Efficacy Of Blood Pressure Management Program (BPMP) In Male Elderly Patients With Known Case Of Hypertension: An Observational Study Journal: Cardiology and Cardiovascular Research Clinical Study: Volume 3, Issue 1, March 2019 Click to Download Full Research Paper Journal Published Link: http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/journal/index?journalid=279 Abstract Around 20% of the population are in prehypertension stage, and nearly 40% of the adult population from Hypertension (HTN). Blood Pressure Management Program (BPMP) is an Ayurvedic treatment strategy using Panchakarma. This study was conducted to evaluate the effect of BPMP on systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mean arterial pressure (MAP), body mass index (BMI) and dependency on conventional therapy in elderly male patients of HTN. This observational study was conducted from January 2017 to February 2018, wherein the data of HTN patients who attended Madhavbaug clinics in Maharashtra, India were identified. Data of patients who were administered BPMP (60-75 minutes) with minimum 6 sittings over 90 days (± 15 days) were considered. Variables were compared between day 1 and day 90 of BPMP. Out of 29 enrolled patients, 24 were finally selected for analysis. BPMP showed significant improvement in SBP by 24.66 (from 150.67 ±12.97 to 126 ± 13.01; p<0.001), DBP by 10.8 (from 87.7917 ±7.72 to 76.917 ±7.59, p< 0.001), MAP by 15.4 (from 108.75 ±7.14 to 93.25 ±8.72, p<0.001). BMI (25.7275 ±2.63 kg/m2 to 24.91 ±2.32 kg/m2), also showed significant reduction. Dependency on concomitant medicines was reduced, with the number of patients on no concomitant medicines increasing from 19% to 29%. BPMP can serve as an effective therapeutic regiment to combat HTN in elderly male patients. Keywords: Blood Pressure Management Program, BPMP, Panchakarma, Hypertension, Systolic, Diastolic, Mean Arterial Pressure, Elderly Male

Original Article: To Study Efficacy of Comprehensive Diabetes Care (CDC) Management Program in Type II Diabetic Obese Patients: An Observational Study Journal: International Journal of Ayurveda and Pharma research. Clinical Study: IJAPR | June 2018 | Vol 6 | Issue 6 Click to Download Full Research Paper Journal Published Link: https://ijapr.in/index.php/ijapr/article/view/937 Abstract Context: Diabetes mellitus (DM) contributes to a major chunk of morbidity, mortality, and healthcare cost on a global level. The prevalence of DM is rising alarmingly, worldwide and India. Comprehensive Diabetes Care (CDC) is a combination of Panchakarma and diet management. Aims: This study was conducted to evaluate the effect of CDC on Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), body mass index (BMI), body weight, abdominal girth and dependency on conventional therapy in DM Patients. Setting and Design: This observational study was conducted in July 2017, wherein the data of obese Type II DM patients (HbA1c >6.5%) who attended out-patient departments (OPDs) at Madhavbaug clinics in Maharashtra, India were identified. Materials and Methods: Data of patients who were administered CDC (60-75 minutes) with minimum 6 sittings over 90 days (± 15 days) were considered. Variables were compared between day 1 and day 90 of CDC. Results: Out of 27 patients, 22 were included for analysis, out of which 10 were males while 12 females. CDC showed significant improvement in HbA1c 1.1% (from 8.80 ± 0.93 to 6.98 ± 1.73; p<0.001), BMI by 2.66 (from 33.79 ± 3.80 to 31.13 ± 3.91, p< 0.001), weight by 6.56 kg (from 83.67 ± 11.28 to 77.11 ± 12.27, p<0.001). Abdominal girth (from 104.34 ± 9.74 to 96.97 ± 11.93; p<0.001), also showed significant reduction. Dependency on concomitant medicines was reduced, with the number of patients on no concomitant medicines increasing from 27% to 41%. Conclusion: Comprehensive Diabetes Care Management Program found to be efficacious; by reducing HbA1c, as well as reducing dependency on allopathic medications. KEYWORDS: Comprehensive Diabetes Care, CDC, Panchakarma, Glycosylated HB, HbA1C, BMI, DM, Alternative Medicine.
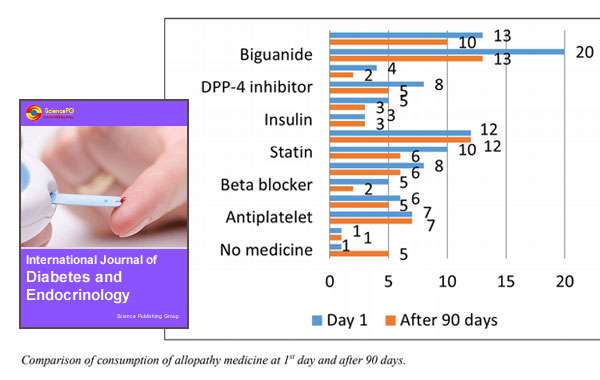
Original Article: Efficacy Of Comprehensive Diabetes Care (CDC) Management Program In Elderly Male Patients Of Type II Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Study Journal: International Journal of Diabetes and Endocrinology Clinical Study: 2018; 3(2): 29-34 Click to Download Full Research Paper Journal Published Link: http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/journal/index?journalid=278 Abstract Globally, Diabetes mellitus (DM) prevalence has created menace, being a major culprit of increased mortality and morbidity and health care expenditures. India is the 2nd country with maximum number of diabetic patients, with an estimated prevalence of around 10%. Comprehensive Diabetes Care (CDC) is a combination of Panchakarma and Diet management. This study was conducted to evaluate the effect of CDC on glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c), body mass index (BMI), body weight, abdominal girth and dependency on conventional therapy in DM Patients. This retrospective study was conducted from July 2017 to January 2018, wherein the data of elderly male type 2 DM patients (HbA1c >6.5%) who attended Madhavbaug clinics in Maharashtra, India were identified. Data of patients who were administered CDC (60-75 minutes) with minimum 6 sittings over 90 days (± 15 days) were considered. Variables were compared between day 1 and day 90 of CDC. Out of 48 enrolled elderly male patients, 34 were included for analysis. CDC showed significant improvement in HbA1c from 8.27 ± 0.96to 7.1 ± 1.30; p=0.0001), BMI from 27.65 ± 3.20 to 25.91 ± 3.29, p< 0.0001), weight from 73.75 ± 10.76to 69.46 ± 10.39, p<0.0001). Abdominal girth (from 100.0 ± 9.08 to 95.36 ± 9.10; p<0.0001), also showed significant reduction. Dependency on concomitant medicines was reduced, with number of patients on no concomitant medicines increasing from 3% to 15%. CDC and allopathy both are found to be efficacious; but CDC acts dually, by reducing HbA1c, as well as reducing dependency on allopathic medications. Keywords: Comprehensive Diabetes Care, CDC, Panchakarma, HbA1C, BMI, DM, Alternative Medicine






