
Sugar is everywhere.In your morning tea. In biscuits. In packaged snacks. In fruit juices. Even in so-called “healthy” breakfast cereals. Yet most people ask me only one question:“Doctor, how much sugar is actually too much?” The problem is that we don’t see sugar clearly. Food labels talk in grams, while our kitchens talk in teaspoons. Once you connect the two, the picture becomes very clear—and often shocking. Converting Sugar: Grams to Teaspoons (The Reality Check) Let’s simplify this. 1 teaspoon of sugar ≈ 4 grams 10 grams = 2.5 teaspoons 20 grams = 5 teaspoons 40 grams = 10 teaspoons The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends limiting added sugar to about 25 grams per day—that’s roughly 6 teaspoons. In real life, many Indians consume two to three times this amount daily, often without realising it. Your Body Does Not Need External Sugar to Survive This surprises many patients. Your body can manufacture its own sugar through a process called gluconeogenesis. The liver converts: Stored glycogen Proteins Fats into glucose as needed. This means refined sugar is not essential for survival. Even if you stop eating sugar completely, your body can still supply glucose for: Brain function Muscle movement Organ activity Sugar is a convenience—not a necessity. How Much Sugar Is Actually Present in Your Blood? An average adult has about 5 litres of blood. At normal fasting levels (around 90 mg/dL), the total amount of sugar circulating in your entire bloodstream is only 4–5 grams. That’s roughly 1 teaspoon of sugar. Your body functions perfectly with just one teaspoon of sugar in circulation at any given time. Now think about what happens when you drink a beverage containing 8–10 teaspoons at once. How Sugar Is Used Inside the Body Once sugar enters the bloodstream, different organs respond: Brain: Uses glucose steadily, not in spikes Muscles: Burn glucose during movement and exercise Liver: Stores excess glucose as glycogen (limited capacity) Pancreas: Releases insulin to control blood sugar Fat cells: Convert excess sugar into stored fat The system works beautifully—until overload becomes routine. What Happens When You Consume Excess Sugar Regularly? Repeated sugar spikes force the pancreas to release insulin again and again. Over time: Cells stop responding efficiently to insulin Insulin resistance develops Blood sugar stays high for longer Insulin resistance is the root cause of: Type 2 diabetes Obesity Fatty liver PCOS High blood pressure Heart disease If this continues unchecked, the pancreas becomes exhausted, leading to chronic high blood sugar. Lessons from Nature Animals like lions, cows, goats, deer, and elephants do not consume refined sugar. Yet they maintain stable metabolic health throughout life. Historically, humans also lived without processed sugar. The sharp rise in diabetes closely mirrors the increase in refined sugar consumption, not natural food intake. So, How Much Sugar Is Too Much? If your bloodstream needs only 1 teaspoon at a time, consuming 8–10 teaspoons in one drink or dessert clearly overwhelms the system. Early warning signs often include: Fatigue after meals Frequent hunger Belly fat Sweet cravings Borderline blood sugar levels Family history of diabetes These are signals, not coincidences. Can Diabetes Be Reversed? Yes—insulin resistance can be reversed, especially in the early and middle stages. This is where structured, root-cause-based care becomes important. Many patients today actively explore Ayurvedic treatment for diabetes because it focuses on correcting metabolism, digestion, lifestyle, and insulin sensitivity—not just suppressing sugar numbers. A Root-Cause Approach to Metabolic Health At Madhavbaug Clinics and Hospitals, we follow a scientifically designed, non-invasive, Ayurvedic-integrated model aimed at: Reducing insulin resistance Improving pancreatic efficiency Supporting liver metabolism Correcting weight and lipid imbalance Protecting long-term heart health This approach complements modern type 2 diabetes treatment by addressing why sugar rises—not just how to lower it temporarily. Thousands of patients have shown improvement in: HbA1c Weight Blood pressure Lipid profile Energy levels and stamina What You Can Do Starting Today Read food labels carefully Convert grams to teaspoons mentally Reduce sugary drinks and packaged foods Eat home-cooked, balanced meals Move your body daily Sleep on time Monitor sugar levels regularly Small daily corrections prevent big future complications. Final Message for Readers Sugar doesn’t harm you overnight.It harms you quietly, daily, and consistently. Understand how much you consume. Respect how little your body actually needs.Correct early—and you can prevent or reverse disease before medication becomes lifelong. Why Your Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT) Matters in Diabetes Reversal A Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT) evaluates how efficiently your body processes sugar after consuming a measured glucose solution. In people with diabetes or prediabetes, the GTT often remains positive due to underlying insulin resistance. At Madhavbaug, our diabetes reversal approach focuses on addressing this root cause. Through structured, non-invasive Ayurvedic protocols aimed at reducing insulin resistance, many patients experience improved sugar metabolism—and over time, some even achieve GTT-negative results under medical supervision.

Many patients walk into my OPD worried and confused.Some panic the moment they hear the words “heart blockage.”Others ask, “Doctor, is a blockage the same as a heart attack?” Let me say this clearly—heart blockage Vs heart attack is one of the most misunderstood topics in cardiac care. And misunderstanding it often leads to dangerous delays. Once you understand the difference, you’ll also see why heart blockage should be managed early—before it becomes an emergency. First Things First: They Are NOT the Same A heart blockage and a heart attack are related—but they are not identical conditions. Think of heart blockage as a slow warning process, and heart attack as a crisis. 1) What Is Heart Blockage? Heart blockage usually means fat plaque buildup inside the coronary arteries, the blood vessels that supply oxygen to your heart muscles. This condition is called atherosclerosis. What Is Fat Plaque Made Of? Fat plaque is a slow-forming mix of: Cholesterol Fat particles Calcium deposits Inflammatory cells This buildup happens gradually over many years, often without obvious symptoms in the early stages. That is why many people live with a blockage without realising it. 2) What Is a Heart Attack? A heart attack is sudden and dramatic. It usually occurs when a blood clot forms abruptly over an existing plaque and completely blocks blood flow to a part of the heart muscle. This can happen in minutes—sometimes even seconds. What Is a Blood Clot Made Of? A blood clot mainly consists of the following: Platelets Clotting proteins like fibrin This is why a heart attack is a medical emergency, requiring immediate hospital care. 3) Fat Plaque vs Blood Clot: The Simplest Explanation Fat Plaque (Heart Blockage) Develops slowly over the years Made mainly of cholesterol and fat Chronic condition May reduce blood flow gradually Not everyone with plaque gets a heart attack Blood Clot (Heart Attack Trigger) Forms suddenly Made mainly of platelets Acute emergency Abruptly blocks the blood supply Can damage the heart muscle within minutes 4) Why This Difference Matters So Much Here’s the most important point I tell my patients: Heart blockage gives you time. A heart attack does not. A blockage is your body’s warning bell.A heart attack is what happens when that warning is ignored for too long. The right strategy is early blockage management, not waiting for a crisis. 5) Can You Have a Blockage Without a Heart Attack? Yes—very commonly. Many people live with heart blockage for years and never experience a heart attack, especially when the blockage is minor. Cholesterol is controlled Sugar levels are managed Weight is reduced Stress and lifestyle factors are corrected Heart attacks usually occur when a plaque becomes unstable and suddenly forms a clot. 6) One Is Chronic, the Other Is Acute Heart blockage → Chronic, progressive condition Heart attack → Sudden, life-threatening emergency Understanding this difference helps patients take action at the right time. 7) Symptoms: When to Rush to the Emergency? Heart Attack Symptoms (Emergency – Act Immediately) Sudden chest pressure or pain Pain spreading to the arm, jaw, neck, or back Profuse sweating Nausea or vomiting Sudden breathlessness Collapse or fainting Call emergency services immediately. Do not wait. Heart Blockage Symptoms (Often Gradual) Breathlessness while walking or climbing stairs Chest heaviness on exertion Easy fatigue Reduced stamina These symptoms are often ignored or attributed to “age” or “lack of fitness”, which is risky. 8) Can Heart Blockage Be Managed Without Surgery? In many stable, non-emergency cases, heart blockage can be managed conservatively under strict medical supervision.Some patients may still require angioplasty or bypass surgery, depending on the severity. However, structured programs focusing on circulation, metabolism, and lifestyle can help selected patients explore heart blockage treatment without surgery—always under doctor guidance. 9) Madhavbaug Khopoli Hospital: Blockage Management Therapy Program At Madhavbaug Khopoli Hospital, we follow a structured, non-invasive, doctor-supervised approach for chronic blockage cases. The programme includes: Blockage Management Therapy Ischemia Reversal Panchakarma Therapy Program 3-Month Reverse Diet Kit The goal is to support: Better blood circulation Reduced cardiac stress Improved stamina and exercise tolerance Better metabolic control (cholesterol, sugar, weight) This approach focuses on long-term stability, not just temporary symptom relief—an integrative model of heart blockage treatment. 10) What Does Research Say? (In Simple Words) Global cardiac research shows that: Plaque progression can be slowed Overall, cardiac risk can be reduced Lifestyle and metabolic correction play a major role Studies related to ischaemia-reversal-based programs have reported improvement in heart function markers in chronic heart disease patients. Important: Results vary based on individual condition, severity, and adherence. 11) A Clear Message for Patients Do not wait for a heart attack to “confirm” heart disease. If you have: Breathlessness on exertion Chest heaviness Fatigue with reduced stamina Your heart may already be asking for help. Book your Blockage Management Evaluation today at Madhavbaug Khopoli Hospital

Compilation of Research Papers presented by Madhavbaug Team at various National and International Research Platforms. Download Research Book

Original Article: Efficacy of Heart Failure Reversal Treatment (HFRT) in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: An Observational Study Journal: International Journal of Applied Research Clinical Study: www.allresearchjournal.com IJAR 2018; 4(7): 297-301 Click to Download Full Research Paper Journal Published Link: http://www.allresearchjournal.com/archives/2018/vol4issue7/PartE/4-7-24-388.pdf Abstract Objective: Heart failure has emerged as global health issue despite multiple treatment options. The present study was conducted to explore the efficacy of heart failure reversal therapy in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Material and Methods: An observational study was conducted in Madhavbaug Hospital, Khopoli from January 2015 to December 2017. All elderly male patients aged>60 years with heart failure and ejection fraction>40% were considered eligible. Patients were hospitalized and HFRT was given twice daily for seven days, following which they were discharged and advised to follow-up at 30, 60 and 90 days. The primary efficacy endpoint was improvement in maximal oxygen uptake (VO2 max) and secondary endpoints were changes in body weight, BMI, abdominal girth, heart rate, blood pressure. Results: A total of 194 patients could complete the entire 90 day treatment and considered for analysis. The VO2max measured at day 90 was significantly higher compared to baseline values (26.36 ± 6.88 versus 18.37 ± 5.47, p<0.001). Such improvement was also observed in bodyweight (64.64 ± 9.22 at day 90 versus 68.69 ± 10.31 at baseline) abdominal girth (90.19 ± 8.46 versus 95.06 ± 9.34) BMI (23.76 ± 2.93 versus 25.23 ± 3.15) heart rate (76.61 ± 14.17 versus 80.66 ± 14.59) systolic BP (122.99 ± 12.56 versus 124.55 ± 15.25) and diastolic BP (78.39 ± 7.67 versus 78.15 ± 8.37) (p value <0.001 for all the secondary endpoints). Conclusion: Our study demonstrated HFRT causes significant improvement in VO2 max in patients with HFpEF which implies better exercise tolerance. HFRT also showed improvement in weight, BMI and abdominal girth, blood pressure of the patients, which could have a positive impact on quality of life. Keywords: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, heart failure reversal therapy, Panchakarma, maximal oxygen uptake

Original Article: Efficacy of Heart Failure Reversal Therapy (HFRT) Program in patients with Preserve Ejection Fraction: An Observational Study Journal: International Ayurveda Publications Clinical Study: RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN 2456-0170, Jul-Aug 2018 Vol III, Issue 4, Ayurpub.com Click to Download Full Research Paper Journal Published Link: https://www.ayurpub.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/1048-1058.pdf Abstract Background: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a worldwide healthcare issue showing growing prevalence, with complex management algorithms. Heart failure reversal therapy (HFRT) is a combination of Panchakarma and allied therapies used by Ayurveda physicians for CHF patients. This observational study was done to evaluate HFRT in HFpEF patients. Study was conducted between January 2017 to December 2017. The data of HFpEF patients who had been administered HFRT with minimum 7 sittings over 90 days (± 15 days) were considered. VO2max, metabolic equivalent (MET), body mass index (BMI), blood pressure (BP), dependency on conventional therapy were compared on day1 and 90. 28 patients were enrolled (21 males, 7 females) with a mean age of 55.79 ± 9.83 years. On analysis, there was significant improvement in mean VO2max (18.16 ± 5.71 vs 31.85 ± 4.80 ml/kg/min, p<0.01) and mean MET (5.19 ± 1.63 vs 9.10 ± 1.37, p<0.01) of the patients on day 90, when compared to day 1. Mean BMI (27.01 ± 3.98 kg/m2 vs 25.69 ± 3.21 kg/m2 , p<0.01) and mean SBP (129.64 ± 15.36 vs 118.79 ± 9.69 mm Hg, p<0.01) were decreased after 90-day HFRT therapy. Dependency on medications was also reduced. To conclude, HFRT is effective in managing HFpEF patients and also decreases the dependency on allopathic medications. KEYWORDS: Heart Failure Reversal Therapy, HFRT, Panchakarma, Chronic Heart Failure, Preserved Ejection Fraction, Ayurveda, Alternative medicine

Original Article: To study the efficacy of Heart Failure Reversal Therapy (HFRT) program in elderly male patients with reduced ejection fraction Journal: International Journal of Medical and Health Research Clinical Study: Volume 4; Issue 7; July 2018; Page No. 149-154 Click to Download Full Research Paper Journal Published Link: http://www.medicalsciencejournal.com/archives/2018/vol4/issue7/4-7-15 Abstract Background and Aims: Some authors consider heart failure (HF) to be a pandemic now, since nearly 26 million people have been affected by it, globally. Out of these, India alone has around 8-10 million patients. Heart Failure Reversal Therapy (HFRT) combines Herbal Panchakarma therapy with Dietary management. This study was conducted to evaluate the effect of HFRT on VO2peak, 6 Minute Walk Test (6MWT), systolic blood pressure (SBP), and diastolic blood pressure (DBP), BMI, weight, abdominal girth, and heart rate. Setting and Design: This observational study was conducted from January 2015 to December 2017, wherein the data of elderly male patients with HF (NYHA class II and III) with reduced ejection fraction (<40%) who attended Madhavbaug hospital, Khopoli, Maharashtra, India were identified. Materials and Methods: Data of patients who were administered HFRT (60-75 minutes) with minimum 7 sittings over 7 days were considered. Variables were compared between day 1, 7, 30, 60 and day 90 of HFRT. Results: 50 elderly males with HF and EF < 40% were enrolled in the study for analysis. There was significant improvement in VO2peak, from 12.71 ± 2.47 at baseline to 14.89 ± 2.05 at day 90 (p<0.001). 6MWT also showed significant improvement from 339.42 ± 106.85 at day 1 to 432.4 ± 89.27 at day 90 (p<0.001). Also, BMI, abdominal girth, weight showed similar statistically significant improvements. Improvements in SBP, DBP and HR were not statistically significant. Conclusion: From the findings of our study, HFRT has been found to be a potent and viable therapeutic alternative for elderly male patients with HF with reduced ejection fraction.

Original Article: To study the efficacy of Ischemia Reversal Program (IRP) in Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD) patients with VO2max and Duke’s Treadmill Score Journal: International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology Clinical Study: August 2018 | Vol 7 | Issue 8 Click to Download Full Research Paper Journal Published Link: https://www.ijbcp.com/index.php/ijbcp/article/view/2704 Abstract Background: Number of people dying from IHD has increased from 0.61 million in 1990 to 1.13 million in 2010, which is a disturbing fact. According to report by World Health Organization, India would be spending a whopping 237 billion US dollars, owing to direct spending on health care and indirectly due to loss of productivity due to IHD. Ischemia Reversal Program (IRP) is a combination of Panchakarma and allied therapy. This study was conducted to evaluate the effect of IRP on VO2max, Duke’s treadmill score, systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), and dependency on conventional therapy in IHD patients. Methods: This observational study was conducted in January 2017, wherein the data of IHD patients (inducible ischemia on stress testing) who attended out-patient departments (OPDs) at Madhavbaug clinics in Maharashtra, India were identified. Data of patients who were administered IRP (60-75 minutes) with minimum 7 sittings over 90 days (±15 days) were considered. Variables were compared between day 1 and day 90 of the IRP. Results: Out of 38 enrolled patients, 25 were males while 13 females. There was significant improvement in Duke’s score with subjects at moderate (50%) and high (31.6%) risk at baseline were significantly decreased to low (52.6%) and moderate (47.4%) after the 90th day of therapy. IRP also showed significant improvement in VO2max by 9.11 (from 20.29±6.72 to 29.40±6.71; p<0.001), SBP by 5.78 (from 128.78±17.40 to 123±12.23, p<0.03), DBP by 4.76 (from 80.53±8.10 to 75.76±6.85, p<0.005). Dependency on concomitant medicines was reduced. Conclusions: IRP was effective in IHD; it had dual benefits, i.e. anti-ischemic effect, as well as reducing the dependency on allopathic medicines. Keywords: Alternative medicine, Blood pressure, Diastolic, Ischemia reversal program, IRP, Ischemic heart disease, IHD, Panchakarma
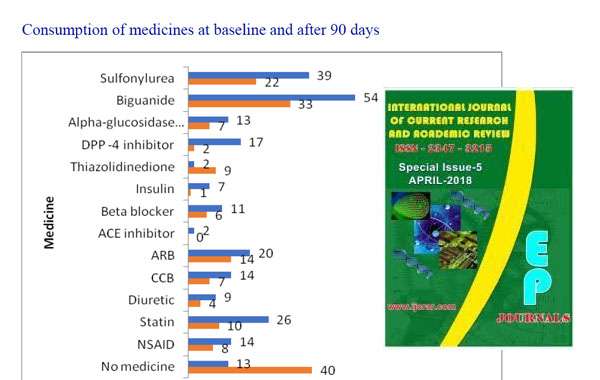
Original Article: Effect of Comprehensive Diabetes Care on Glycaemic Control with Reduction in Dependency of Oral Hypoglycaemic Medicines in Pre-obese Diabetic Patients: A Retrospective Study Journal: International Journal of Current Research and Academic Review Clinical Study: Int.J.Curr.Res.Aca.Rev.2018; 6(11): 73-81 Click to Download Full Research Paper Journal Published Link: http://www.ijcrar.com/6-11-2018/Rohit%20Sane,%20et%20al.pdf Abstract Although multiple new drugs are coming out in the market, India has the 2nd highest number of diabetics in the world.The aim of this study was to evaluate effects of Comprehensive Diabetes Care (CDC) on Glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c) and metabolic parameters in pre-obese diabetic patients. In this retrospective study, data of pre-obese DM patients who had received 6 CDC sittings over 90 days in the out-patient departments (OPDs) at Madhavbaug clinics was collected between May 2013 to April 2018. Demographic and co-morbidity details were noted. HbA1c, body mass index (BMI), abdominal girth, systolic and diastolic blood pressure (SBP, DBP), dependency on medications were assessed on days 1 and 90 of CDC. The patients followed a specific low-calorie diet plan during the study. 89 participants, (52 males, 37 females) were enrolled. Mean HbA1c measured at day 90 was significantly lower than that on day 1 (6.86 ± 1.24 vs 9.02 ± 1.79, p<0.001). Mean BMI was significantly reduced on day 90 when compared to baseline (25.39 ± 1.53 vs 27.24 ± 1.33, p<0.001). Abdominal girth was significantly decreased on day 90 compared to baseline (91.64 ± 6.26 vs 97.12 ± 7.03, p<0.001). SBP (122.83 ± 13.56 vs 131.60 ± 16.10, p<0.001) and DBP (77.02 ± 6.81 vs 81.75 ± 9.43, p<0.001) were also significantly decreased after 90 days. Dependency on concomitant medicines was reduced. Glycaemic control and metabolic parameters significantly improved after 90-day CDC treatment. Reduction in blood pressure and intake of concomitant medications were also noted. Keywords: Comprehensive diabetes care, CDC, Panchakarma, Diabetes mellitus, HbA1c, Body mass index, Ayurveda, Alternative medicine

Original Article: Effect of Heart Failure Reversal Therapy Program (HFRT) on Chronic Heart Failure Patients: A Retrospective Study Journal: Journal of research in Traditional Medicine Clinical Study: J. res. tradit. med. | Volume 4 | Issue 2 | Mar – Apr 2018 Click to Download Full Research Paper Journal Published Link: http://www.allresearchjournal.com/archives/2018/vol4issue7/PartE/4-7-24-388.pdf Abstract Background: Chronic heart failure (CHF) is a major health issue despite of the available medications. Heart failure reversal therapy (HFRT), a combination of herbal treatment and allied therapies, has been advocated by Ayurveda physicians as an add-on therapy for CHF. Aim: The present study was conducted to evaluate the effect of HFRT on Maximum Aerobic Capacity (MAC), blood pressure (BP), body mass index (BMI) and dependency on conventional therapy in CHF Patients. Materials & Methods: The present retrospective study was conducted in July 2017, wherein the data of CHF patients (New York Heart Association, NYHA Class I–IV) who attended out-patient departments (OPDs) at Madhavbaug clinics in Maharashtra, India were identified. Data of patients who were administered HFRT (60-75 minutes) with minimum 7 sittings over 90 days (± 15 days) were considered. Variables were compared between day 1 and day 90 of HFRT. Observations and Results: Out of 79 patients included, 39 were males while 40 females. HFRT showed significant improvement in MAC by 50.35% (from 18.60(±7.01) to 27.97(±7.98), p<0.01) with maximum improvement in NYHA Grade IV patients (n=14) [change by 145.90% (from 7.46 to 18.36, p<0.01)]. BMI [27.78(±5.50) kg/m2 to 26.61(±4.84) kg/m2], systolic and diastolic blood pressure [134.4(±17.2) mm Hg to 122.5(±9.74) mm Hg and 82.75 (±7.13) mm Hg to 77.97(±10.73) mm Hg, (p<0.01) respectively] showed significant reductions. Dependency on concomitant medicines was reduced, with number of patients on no concomitant medicines increasing from 19% to 42%. Conclusion: HFRT can be an effective option for management of CHF patients, along with conventional allopathic medications. Keywords: Alternative medicine, Chronic heart failure, Heart failure reversal therapy, Maximum aerobic capacity, Panchakarma

Original Article: To Evaluate the Efficacy of Heart Failure Reversal Therapy Using NT-Probnp Levels in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure Journal: Cardiology and Cardiovascular Research Clinical Study: 2018; 2(3): 61-64 sciencepublishinggroup.com doi: 10.11648/j.ccr.20180203.13 Click to Download Full Research Paper Journal Published Link: http://article.sciencepublishinggroup.com/pdf/10.11648.j.ccr.20180203.13.pdf Abstract Heart failure is considered as a life-threatening epidemic disorder affecting about 26 million world’s population and associated with considerable morbidity, mortality and healthcare expenses. Despite the availability of a range of advanced treatments and sophisticated therapies the prevalence of heart failure represents a herculean challenge. To address the challenge, the current investigation was conducted by evaluating the efficacy of Heart Failure Reversal Therapy (HFRT) in reducing left ventricular distress by assessing N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels in congestive heart failure (CHF) patients. Total 76 CHF patients with NYHA Class II and III were screened from March to May 2017 and 15 CHF patients with NT-proBNP = 300-1500 pg/ml were selected for the study. NT-proBNP is measured as a marker, the value of which increases with an increase in severity of CHF. The study therapy, HFRT comprises of traditional procedure of panchkarma that includes snehana (external oleation), swedana (passive heat therapy), hrudaydhara (concoction dripping treatment) and basti (medicated enema) was administered twice daily for 7 days. Post-HFRT, ARJ kadha was administered for next 12 weeks follow-up. NT-proBNP levels were measured after a follow-up period of 90 days along with some other parameters like BMI, VO2peak (evaluated by cardiac stress test with modified Bruce protocol) and weight. The findings of the investigation revealed significant reduction in NT-proBNP levels (42.46%, p = 0.009), weight (4.82%, p = 0.0007) and BMI (3.67%, p = 0.034) at the end of the follow-up period. The study also yielded significant improvements in VO2peak (50.96%, p = 0.004). The overall results suggest that HFRT can possibly be explored as add-on therapy or a feasible alternative for the effective management of CHF. Keywords: NT-proBNP, Chronic Heart Failure, Heart Failure Reversal Therapy











