
How Much Sugar Is Too Much?
Sugar is everywhere.In your morning tea. In biscuits. In packaged snacks. In fruit juices. Even in so-called “healthy” breakfast cereals.
Please note, due to Diwali Holidays , there may be delays in processing and delivering orders. We appreciate your patience !
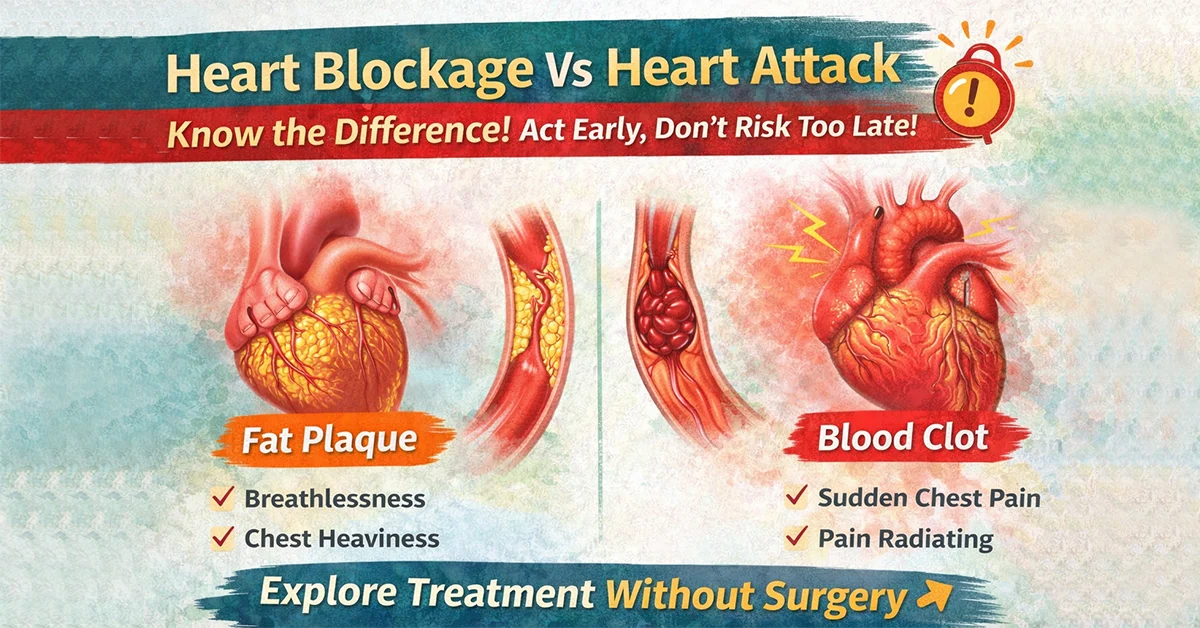
Table of Contents
ToggleMany patients walk into my OPD worried and confused.
Some panic the moment they hear the words “heart blockage.”
Others ask, “Doctor, is a blockage the same as a heart attack?”
Let me say this clearly—heart blockage Vs heart attack is one of the most misunderstood topics in cardiac care. And misunderstanding it often leads to dangerous delays.
Once you understand the difference, you’ll also see why heart blockage should be managed early—before it becomes an emergency.
A heart blockage and a heart attack are related—but they are not identical conditions.
Think of heart blockage as a slow warning process, and heart attack as a crisis.
Heart blockage usually means fat plaque buildup inside the coronary arteries, the blood vessels that supply oxygen to your heart muscles.
This condition is called atherosclerosis.
Fat plaque is a slow-forming mix of:
Cholesterol
Fat particles
Calcium deposits
Inflammatory cells
This buildup happens gradually over many years, often without obvious symptoms in the early stages.
That is why many people live with a blockage without realising it.
A heart attack is sudden and dramatic.
It usually occurs when a blood clot forms abruptly over an existing plaque and completely blocks blood flow to a part of the heart muscle.
This can happen in minutes—sometimes even seconds.
A blood clot mainly consists of the following:
Platelets
Clotting proteins like fibrin
This is why a heart attack is a medical emergency, requiring immediate hospital care.
Develops slowly over the years
Made mainly of cholesterol and fat
Chronic condition
May reduce blood flow gradually
Not everyone with plaque gets a heart attack
Forms suddenly
Made mainly of platelets
Acute emergency
Abruptly blocks the blood supply
Can damage the heart muscle within minutes
Here’s the most important point I tell my patients:
Heart blockage gives you time. A heart attack does not.
A blockage is your body’s warning bell.
A heart attack is what happens when that warning is ignored for too long.
The right strategy is early blockage management, not waiting for a crisis.
Yes—very commonly.
Many people live with heart blockage for years and never experience a heart attack, especially when the blockage is minor.
Cholesterol is controlled
Sugar levels are managed
Weight is reduced
Stress and lifestyle factors are corrected
Heart attacks usually occur when a plaque becomes unstable and suddenly forms a clot.
Heart blockage → Chronic, progressive condition
Heart attack → Sudden, life-threatening emergency
Understanding this difference helps patients take action at the right time.
Sudden chest pressure or pain
Pain spreading to the arm, jaw, neck, or back
Profuse sweating
Nausea or vomiting
Sudden breathlessness
Collapse or fainting
Call emergency services immediately. Do not wait.
Breathlessness while walking or climbing stairs
Chest heaviness on exertion
Easy fatigue
Reduced stamina
These symptoms are often ignored or attributed to “age” or “lack of fitness”, which is risky.
In many stable, non-emergency cases, heart blockage can be managed conservatively under strict medical supervision.
Some patients may still require angioplasty or bypass surgery, depending on the severity.
However, structured programs focusing on circulation, metabolism, and lifestyle can help selected patients explore heart blockage treatment without surgery—always under doctor guidance.
At Madhavbaug Khopoli Hospital, we follow a structured, non-invasive, doctor-supervised approach for chronic blockage cases.
Blockage Management Therapy
Ischemia Reversal Panchakarma Therapy Program
3-Month Reverse Diet Kit
The goal is to support:
Better blood circulation
Reduced cardiac stress
Improved stamina and exercise tolerance
Better metabolic control (cholesterol, sugar, weight)
This approach focuses on long-term stability, not just temporary symptom relief—an integrative model of heart blockage treatment.
Global cardiac research shows that:
Plaque progression can be slowed
Overall, cardiac risk can be reduced
Lifestyle and metabolic correction play a major role
Studies related to ischaemia-reversal-based programs have reported improvement in heart function markers in chronic heart disease patients.
Important: Results vary based on individual condition, severity, and adherence.
Do not wait for a heart attack to “confirm” heart disease.
If you have:
Breathlessness on exertion
Chest heaviness
Fatigue with reduced stamina
Your heart may already be asking for help.
Book your Blockage Management Evaluation today at Madhavbaug Khopoli Hospital
Disclaimer: The content on this website is for informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for medical advice. Please consult a qualified Madhavbaug Ayurvedic doctor before starting any treatment.
Table of Contents
Toggle
Sugar is everywhere.In your morning tea. In biscuits. In packaged snacks. In fruit juices. Even in so-called “healthy” breakfast cereals.

Ayurveda Transformed Life After Heart Attack — यह रियल रिकवरी स्टोरी दिखाती है कि सही समय पर medical guidance, lifestyle